Save the Western Ghats Movement and Citizens for Alternatives to Nuclear Energy
Item
- Title
- Save the Western Ghats Movement and Citizens for Alternatives to Nuclear Energy
- Date
- 1986
- extracted text
-
THE
SAVE
MOVEMENT
GHATS
WESTERN
AND
CITIZENS
FOR
ALTERNATIVES TO NUCLEAR ENERGY
We present below a summary of facts (with sources) to show why.
-^"nuclear energy must not be proliferated any further in India.
I.
Do we need to generate more energy or do we need to use
available energy most efficiently ?
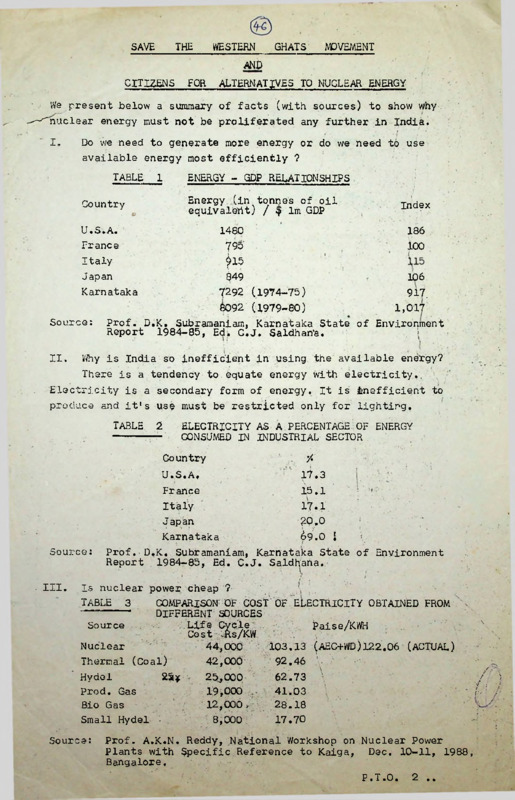
TABLE
1
ENERGY - GDP RELATIONSHIPS
Energy (in tonnes of oil
equivalent) / $ Im GDP
Country
£>
U.S.A.
France
Italy
Japan
Karnataka
Source:
1480
. 79o
|15
Index
186
100
.
849
106
7292 (1974-75)
917.
8092 (1979-80)
1,017
Prof. D.K. Subramaniam
1CUU.CU11, Karnataka State of Environment
Report
1984-85, FEd. C.J. Saldhan’a.
:
, *
Why is India so inefficient in using the available energy?
There is a.tendency to equate energy with electricity,,
Electricity is a secondary form of energy. It is inefficient to
produce and it's use must be restricted only for lighting.
II.
TABLE. 2
Source:
. III.
ELECTRICITY AS A PERCENTAGE OF ENERGY
CONSUMED IN INDUSTRIAL SECTOR
Country
■A
U.S.A.
France
Italy
Japan
Karnataka
17.3
15.1
17.1
2-0.0
69.0 I
Prof. D.K. Subramaniam, Karnataka State of Environment
Report 1984-85, Ed. C.J. Saldhana.
Is nuclear power cheap ?
TABLE 3
<COMPARISON^ OF COST OF ELECTRICITY OBTAINED FROM '
DIFFERENT SOURCES
Source
.Life Cycle'
Paise/KWH
Cost -Rs/KW
Nuclear
44,000
103.13 (aEC+WD)122.06 (ACTUAL)
42,000
Thermal (Coal)
92.46 '•
Hydel
22$
25,000
62.73
Prod. Gas
Bio Gas
Small Hydel •
Source:
19,000
12,000>
8,000
41.03
28.18
17.70
Prof. A.K.N. Reddy, National Workshop on Nuclear Power
Plants with Specific Reference to Kaiga, Dec. 10-11, 1988,
Bangalore.
P.T.O.
2 ..
/r - •
$1
Page
2
IV.
Are nuclear plants safe,?.
India is currently installing the Canadian designed CANDU
REACTORS. The performance of-these reactors in Canada vis-a-vis
their accident proneness is given below :
TABLE
4
CALCULATED' PROBABILITIES OF ACCIDENTS IN CANDU
REACTORS
■ 20 Reactors
20 Reactors
Type of Accident
(Annual)
(Life Time)
Loss of coolant
1/5
99.7/
(Three-Mile Island)
Core Meltdown (Chernobyl) -i-'
1/500
7/
Source: Atomic Energy of Canada Ltd., Safety Report for Lepreau-1,
1979. Presented by Dr. Vishnu Kamath, National Workshop
on Nuclear Power Plants with Specific Reference to Kaiga,
Dec. 10 and 11, 1988, Bangalore.
V.
Accidents and Consequences •:
Chernobyl
- Estimated Cost $ 17000 m
1,35,000 people evacuated.
Imniediate deaths 33.
Cancer related mortality 1500-500000.
Estimated death toll in a populated site such as in India 500000 to 1000000..
Can we afford this economic and social cost? U. •
Source: Christopher Flavin, World Watch Institute, Science Age,
September 1987.
VI.
Unanswered Questions
1.
How do you treat nuclear waste? There is no known method.
Nuclear waste can only be contained (disposed). Containment
does not mitigate itfs harmful nature.
2.
How long does nuclear waste need to be contained? While high
level wastes have to be contained for eternity, an optimistic
estimate is atleast 6,000 years.
3.
NO •
Do we have containers that last 6,000 years?
4.
The life of a nuclear reactor is only 30 years♦ What happens
to the reactor at the end of its life ?
It is left as such and buried under a sarcophagus and will
need to be guarded for 6,000 years against vandals, terrorists,
earthquakes and other acts 'of God.
VII. CRISIS MAIMAGEMENT
We cannot even fight fires in -a high rise building (Hotel
Siddhartha Fire, New Del hi) , We, cannot handle gas leaks (Union
Carbide, Bhopal). Can we deal with nuclear accidents?
'
"
‘
*
To know how Soviet Union dealt with Chernobyl, read National
Geographic, May 1987; Christian Science Monitor, May 1, 1989•
If you want more details of the original literature, please
write to :
DR. VISHNU KAMATH,
456,
VIVEK NAGAR,
BANGALORE - 560 047.
Position: 574 (24 views)